Biceps Tendonitis
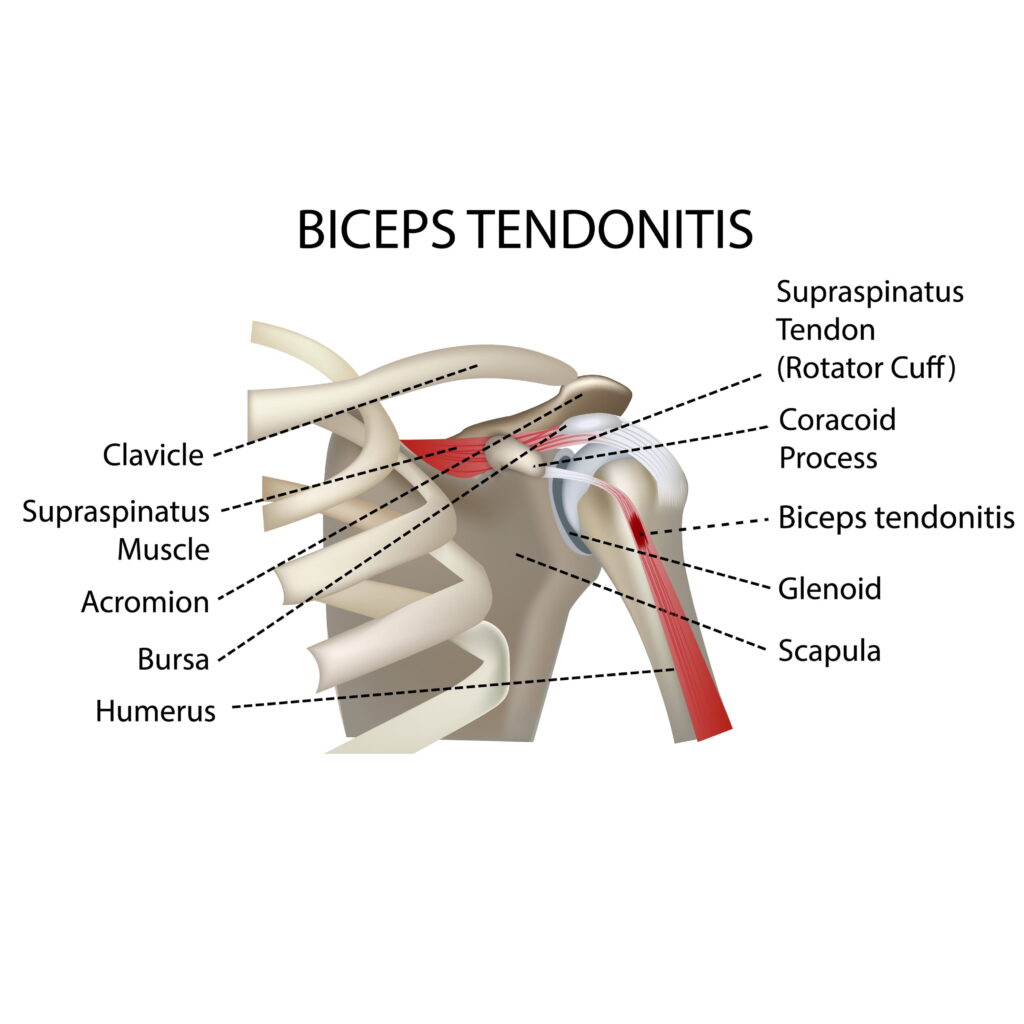
Bicep Tendonitis
If you have been experiencing pain in your bicep, you may have tendonitis. This condition can be very frustrating and painful, but there are treatments available that can help. Read on to learn more about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bicep tendonitis.
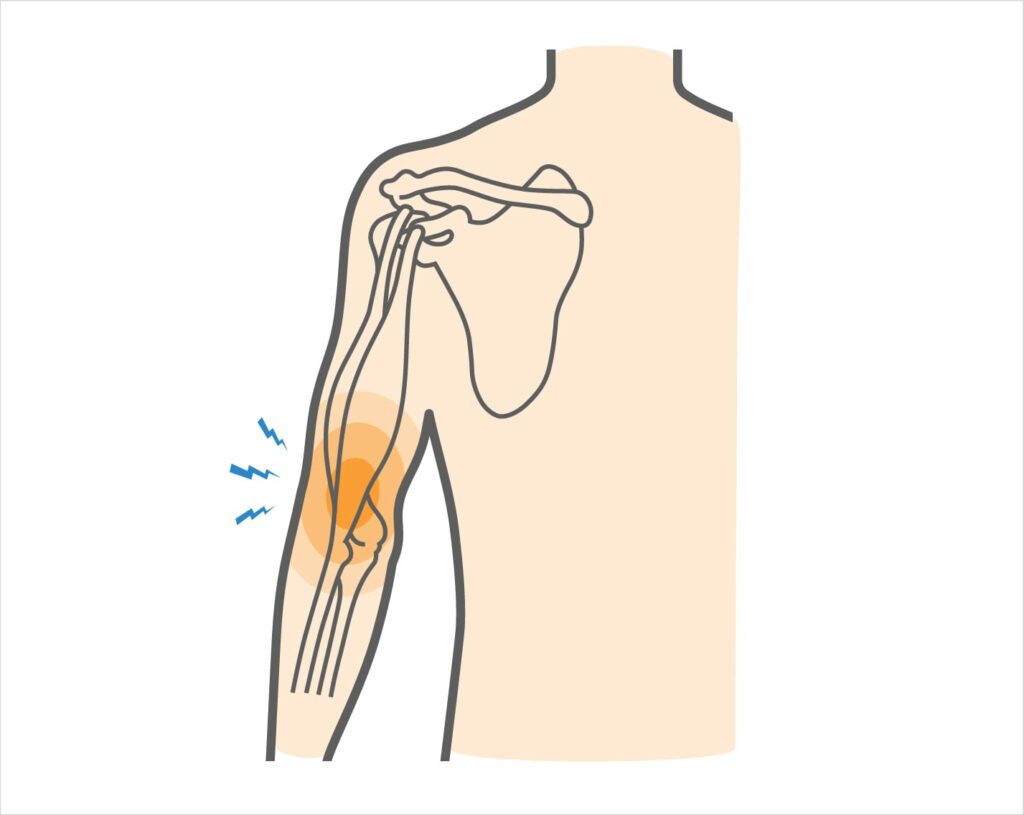
Bicep tendonitis: An overview
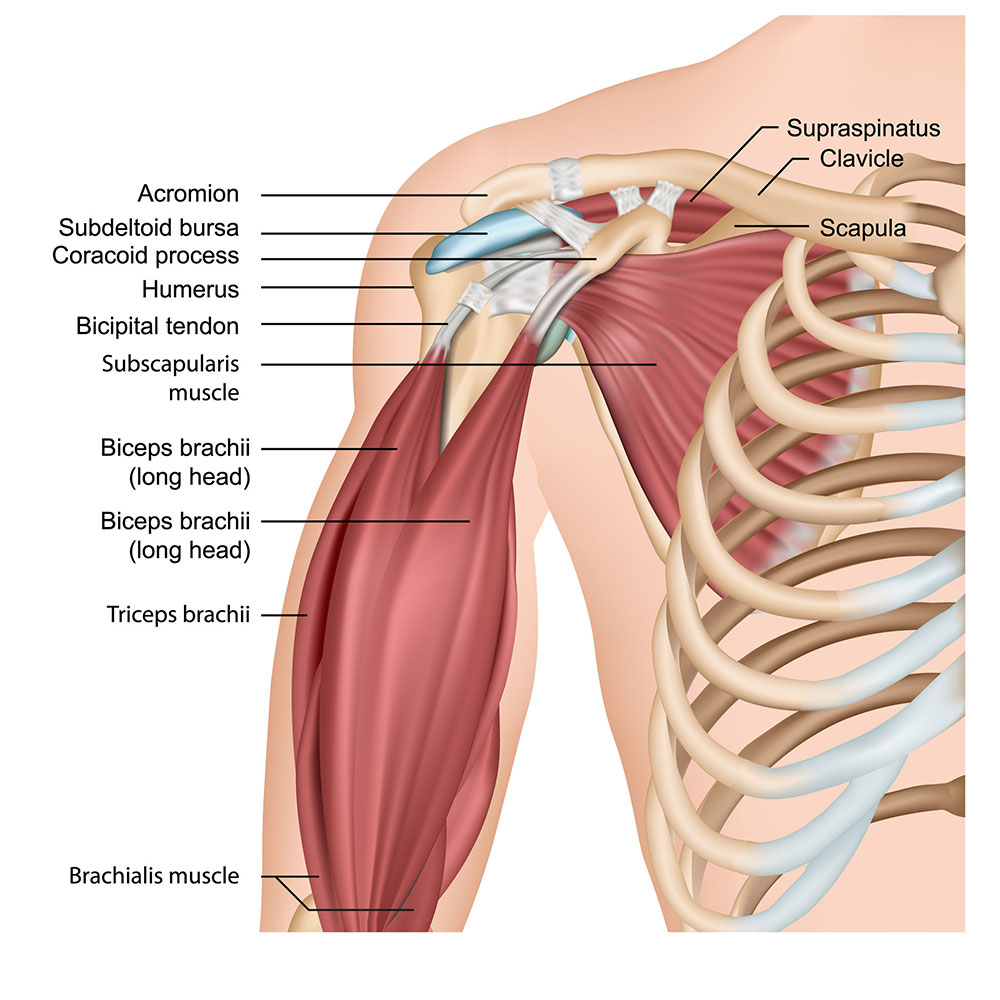
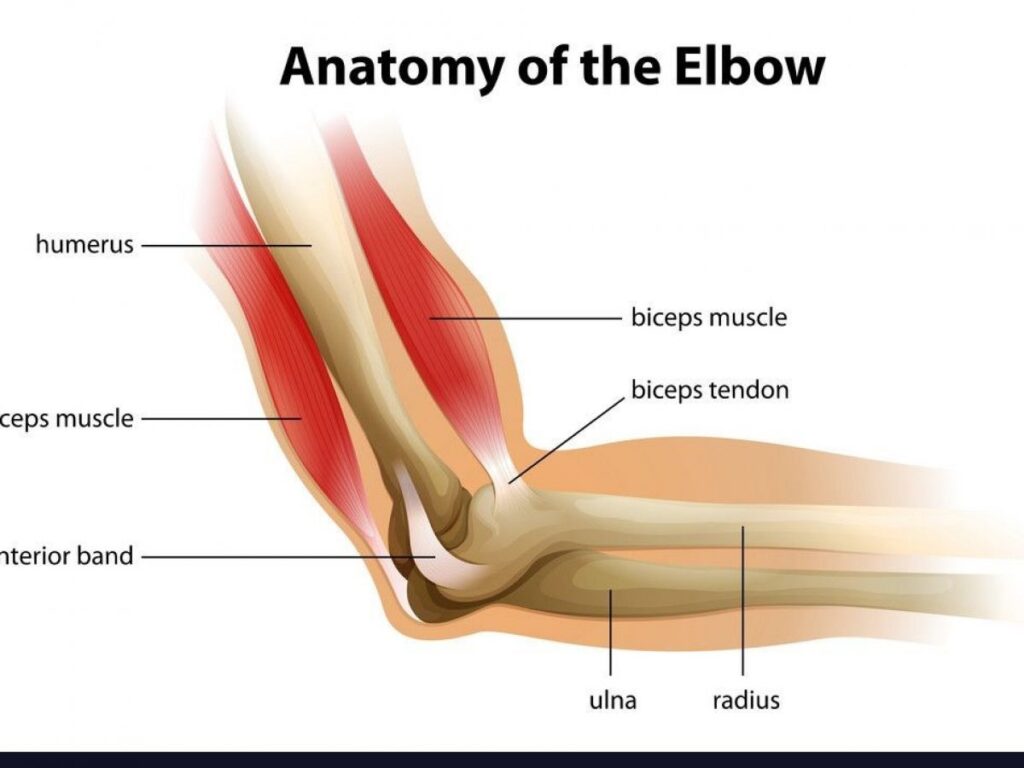
Biceps tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the biceps tendon. This tendon is located in the shoulder and attaches the biceps muscle to the bone. Bicep tendonitis can be caused by overuse, repetitive motions, or injury.
There are two types of bicep tendonitis:
- Distal bicep tendonitis:
This type of bicep tendonitis affects the portion of the biceps tendon that attaches to the bone in the elbow.
- Proximal biceps tendonitis:
This type of bicep tendonitis affects the portion of the biceps tendon that attaches to the shoulder.
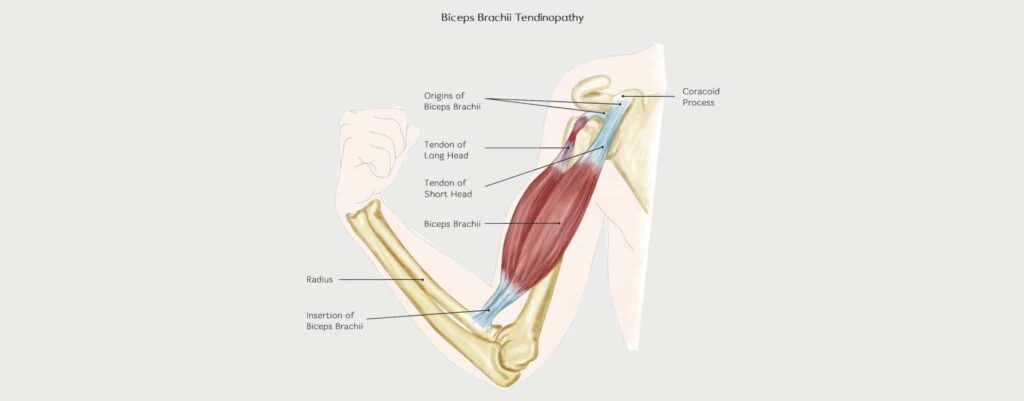
Symptoms of bicep tendonitis
Symptoms of bicep tendonitis may include:
– Pain in the shoulder or elbow
– Inflammation or tenderness in the shoulder or elbow
– Weakness in the arm
– Creaking or cracking sound when moving the arm
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor. Bicep tendonitis is a treatable condition, but if left untreated, it can lead to more serious problems.
Causes of bicep tendonitis:
Several factors can contribute to the development of bicep tendonitis.
1. Overuse:
One of the most common causes of bicep tendonitis is overuse. This can occur from participating in activities that put repetitive stress on the biceps tendon, such as weightlifting, throwing, or tennis.
2. Age:
As we age, the tendons become less flexible and more susceptible to injury. This can lead to the development of bicep tendonitis.
3. Injury:
An injury to the biceps tendon can also cause bicep tendonitis. This can occur from a fall, direct blow, or overstretching of the tendon.
4. Anatomy:
Certain anatomical factors can increase your risk of developing bicep tendonitis. This includes having a shallow groove in the shoulder joint where the biceps tendon attaches (a condition called glenohumeral dysplasia), or having a small area of bone attachment on the biceps tendon (a condition called partial avulsion).
5. Medical conditions:
Certain medical conditions can increase your risk of developing bicep tendonitis. This includes rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes.
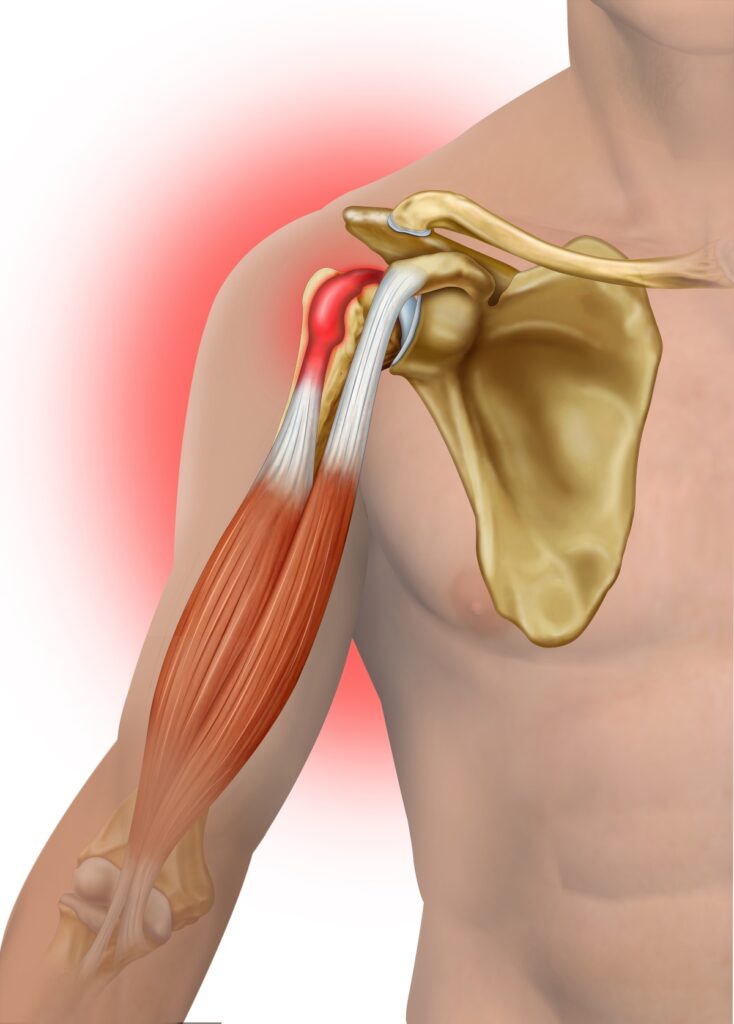
Diagnosis of Bicep Tendonitis
Bicep tendonitis is diagnosed through a combination of a medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests.
Medical history:
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and when they started. They will also ask about your past medical history, including any previous injuries or surgeries.
Physical examination:
Your doctor will examine your shoulder for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. They may also test your strength by having you lift your arm against resistance.
Imaging tests:
Your doctor may order X-rays or an MRI to rule out other conditions and to get a better look at the condition of your bicep tendon.
Get rest:
Rest is important to allow your body to heal. You may need to take a break from activities that put stress on your bicep tendon, such as weightlifting or throwing.
Treatment for bicep tendonitis:
The goal of bicep tendonitis treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation and to promote healing of the biceps tendon. Treatment options include:
- Rest:
Resting from activities that aggravate the condition is important in the treatment of bicep tendonitis. This will allow the inflammation to go down and the tissue to heal.
- Ice:
Applying ice to the affected area several times a day can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Compression:
Compressing the affected area with an elastic bandage can also help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Elevation:
Elevating the affected arm above the level of the heart can also help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- NSAIDs:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can be helpful in reducing pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy:
Working with a physical therapist can help to strengthen the muscles and tendons around the biceps tendon, which can help to prevent further injury. Physical therapy may also include exercises to improve range of motion and flexibility.
- Surgery:
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the biceps tendon. This is typically only recommended if other treatment options have failed to improve symptoms.
Prevention of bicep tendonitis:
There are several things you can do to help prevent the development of bicep tendonitis. This includes:
1. Warm up before activity:
Warming up with a light jog or dynamic stretching before participating in activities that put stress on the biceps tendon can help to prevent injury.
2. Use proper form:
Using proper form when participating in activities that put stress on the biceps tendon can also help to prevent injury. This includes avoiding activities that require excessive force or range of motion.
3. Strength training:
Strengthening the muscles and tendons around the biceps tendon can help to prevent injury. This can be done with exercises such as curls, triceps extensions, and shoulder presses.
4. Cross-training:
Participating in a variety of activities that put stress on different muscle groups can help to prevent overuse injuries. This includes activities such as swimming, biking, and elliptical training.
5. Wearing proper equipment:
Wearing proper equipment when participating in activities that put stress on the biceps tendon can help to prevent injury. This includes using weightlifting gloves when lifting weights and using an elbow pad when playing tennis.
6. Rest:
Allowing the biceps tendons and muscles to rest when they are sore can help to prevent further injury. This includes avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and taking breaks during extended periods of activity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bicep tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of the bicep tendon, the tissue that connects the biceps muscle to the shoulder. The condition mostly occurs in the long head of the biceps and can cause pain and tenderness in the shoulder and upper arm. Bicep tendonitis is often caused by overuse of the arm, such as from weightlifting or throwing. It can also be caused by an injury to the arm.
The main symptom of bicep tendonitis is pain in the shoulder and upper arm. The pain may be dull and achy, or it may be sharp and searing. The pain may worsen with activity, such as lifting weights or throwing a ball. You may also feel tenderness when you press on the affected area. In some cases, you may hear a snapping or popping sound when you move your arm.
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history to diagnose biceps tendinitis. He or she will also do a physical examination. The examination will likely include moving your arm in different ways to see where the pain is coming from. Your doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an MRI or ultrasound, to take a closer look at the tendon injuries.
The goal of treatment for bicep tendinitis is to reduce shoulder pain and inflammation. Treatment options include rest, icing the affected area, and taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications. You may also need physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons around the shoulder. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the bicep tendon.
If bicep tendonitis is left untreated, it can lead to further damage to the bicep tendon. This can eventually cause the biceps tendon tear or even a rupture. Bicep tendonitis can also make it difficult to move your arm, which can lead to loss of function in the arm.
There are several things you can do to help prevent biceps tendinitis. First, warm up before you participate in any activities that may put stress on your shoulder. Second, use proper form when lifting weights or doing other activities that require arm movement. Third, take breaks often if you are participating in an activity that repetitively stresses the shoulder. Fourth, stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons around the shoulder on a regular basis. Finally, see your doctor if you develop any pain or inflammation in the shoulder.
If you have bicep tendonitis, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment. With proper treatment, the condition can often be resolved without complication. However, if bicep tendonitis is left untreated, it can lead to further damage to the bicep tendons (biceps brachii) and loss of function in the arm. If you are concerned about developing bicep tendonitis, talk to your doctor about ways to prevent the condition.
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us




