Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects the hands and wrists. It can cause pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hands and wrists. If left untreated, CTS can lead to permanent damage to the nerves and muscles in the hands. Thankfully, there are several treatment options available for CTS, including surgery and conservative treatments like splints and physical therapy.
This guide will provide you with everything you need to know about CTS, from causes to treatment options.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: An introduction
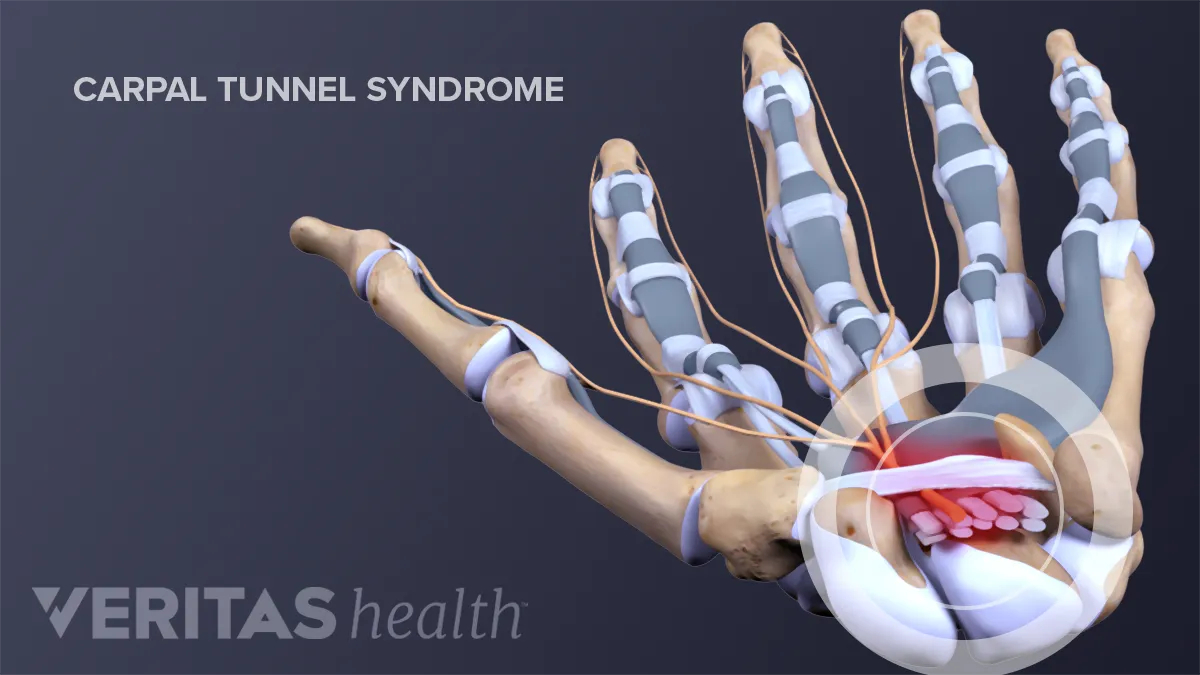
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed. This can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers.
The condition is seen more often in women than men and is more common in people over the age of 40.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome typically begin gradually and worsen over time. They may include:
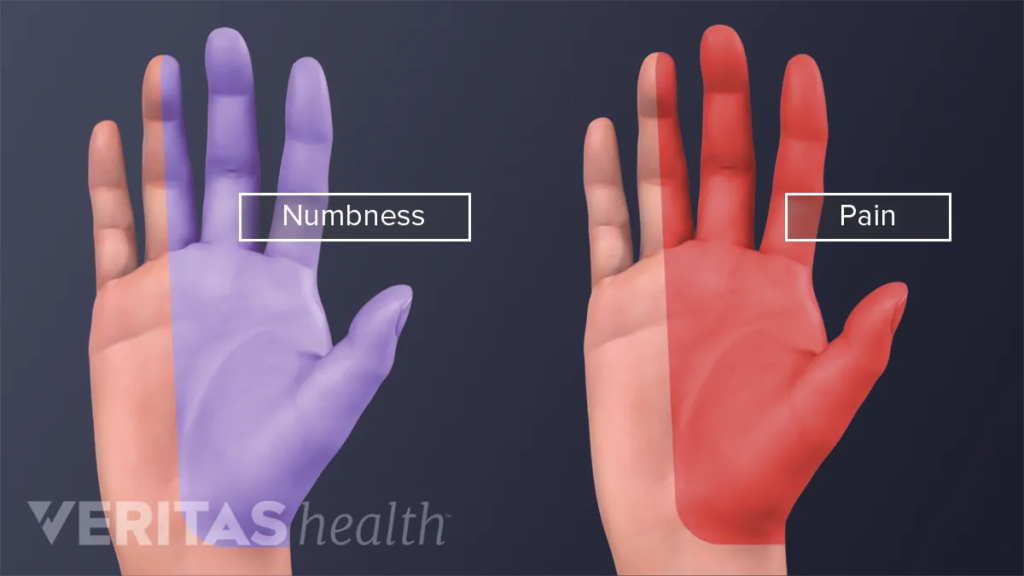
- Numbness or tingling in the hand and fingers
- Pain in the hand, wrist, or forearm
- Weakness in the hand or fingers
If carpal tunnel syndrome is left untreated, it can lead to permanent nerve damage.
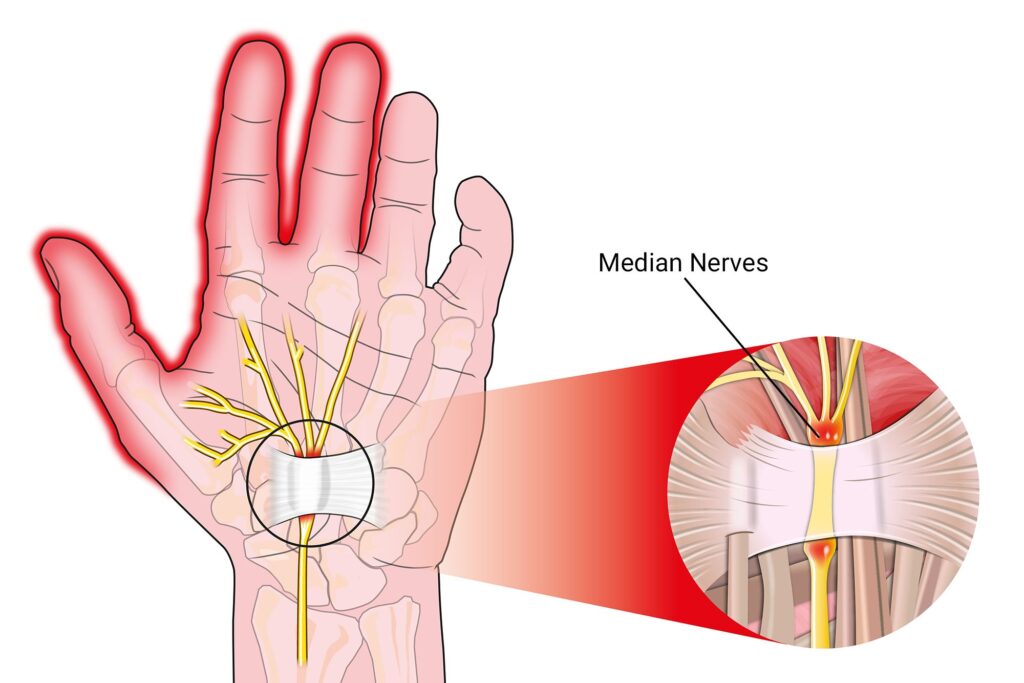
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Medical history:
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and when they began. He or she will also ask about your past medical history, including any previous injuries or conditions that may be causing or contributing to your carpal tunnel syndrome.
Physical examination:
During the physical examination, your doctor will check for specific signs of carpal tunnel syndrome. These signs include tenderness in the wrist and hand, weakness in the muscles of the hand and fingers, and decreased sensation in the hand.
Diagnostic tests:
In some cases, your doctor may recommend one or more diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. These tests may include electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies. EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles, while nerve conduction studies measure how well nerves are able to send electrical signals. New technology testing machines with high performance, a relevant certification, and accurate test data make the diagnosis a lot easier.
Once carpal tunnel syndrome is diagnosed, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that best meets your needs.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand and arm. The carpal tunnel is a narrow, tube-like passageway in the wrist that protects the nerve that controls movement in the hand. When this nerve becomes compressed or pinched, it can cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
There are several treatment options available for carpal tunnel syndrome. Some people may need medication to relieve symptoms, while others may require surgery to release the pressure on the nerve. In some cases, a combination of both medication and surgery may be necessary.
The first step in treating carpal tunnel syndrome is to identify and avoid activities that trigger or aggravate symptoms. If possible, these activities should be avoided altogether. However, if they cannot be avoided, it is important to take frequent breaks and to use proper ergonomic techniques to minimize stress on the wrist and hand.
If symptoms are severe, medication may be necessary to relieve pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can be effective in reducing swelling and pain. A direct injection of steroid into the carpal tunnel area may also be beneficial.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to release the pressure on the nerve. This procedure is called carpal tunnel release surgery. It is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, meaning you will not need to stay in the hospital overnight. Recovery from carpal tunnel release surgery takes several weeks, but most people experience a significant decrease in pain and other symptoms.
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel release surgery is a procedure that releases this pressure on the nerve, providing relief from symptoms.
Carpal tunnel release surgery is generally considered to be a safe and effective treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. The vast majority of patients who undergo the procedure experience significant improvements in their symptoms. In some cases, however, symptoms may persist or even worsen after surgery. If this occurs, additional treatment options such as physical therapy or medications may be recommended.
If you are considering carpal tunnel release surgery, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with your doctor. He or she can help you make an informed decision about whether or not this treatment is right for you.
Risk Factors for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
As with any condition, certain factors may increase your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Some of these include:
Age
With age, the tissues in your body become less flexible and more brittle. This can lead to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Gender
Women are three times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than men.
Family history
If you have a family member who has had carpal tunnel syndrome, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
Certain medical conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid problems can increase your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Repetitive motions
Any type of work or activity that requires you to repeat the same motions over and over again can put you at risk for carpal tunnel syndrome. This includes typing, knitting, and painting.
Obesity
People who are obese are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than those who are at a healthy weight.
If you have any of these risk factors, it’s important to be aware of the potential for developing carpal tunnel syndrome. If you start to experience any symptoms, be sure to see your doctor so that you can get treatment as soon as possible.
Prevention Tips for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Following are some tips that may help you avoid or reduce your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Keep your wrists in a neutral position. Avoid bending them up or down for long periods of time.
- Take frequent breaks from activities that require repetitive hand motions, such as typing on a keyboard or using a mouse.
- Use ergonomic keyboards, mice, and other office equipment designed to minimize stress on the hands and wrists.
- Exercise your hands and wrists regularly to keep them strong and flexible.
- Wear splints at night to keep your wrists in a neutral position while you sleep.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the wrists from excess body weight.
- Talk to your doctor about medications that can help relieve pain and inflammation associated with carpal tunnel syndrome.
If you have carpal tunnel syndrome, these prevention tips may help reduce your symptoms and slow the progression of the condition. However, it’s important to consult with your doctor for specific treatment recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed. This can cause tingling, numbness, and pain in the affected hand.
Anyone can develop carpal tunnel syndrome, but it is more common in women and people over the age of 40. People who have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, are also at greater risk.
The most common symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome is pain or numbness in the hand and wrist. This can occur when the median nerve becomes compressed. Other symptoms may include weakness in the hand and difficulty gripping objects.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and nerve testing. Your doctor may also order X-rays or MRI to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of your symptoms. In some cases, splinting or corticosteroid injections may be enough to ease pain and inflammation. Surgery may be necessary for more severe cases.
There is no sure way to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk. If you have a job that requires repetitive hand motions, take frequent breaks to stretch your hands and wrists. And if you have any medical conditions that put you at greater risk, be sure to follow your doctor’s recommendations for treatment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can cause permanent damage to the median nerve if it is not treated properly. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve. With proper treatment, most people are able to recover fully from carpal tunnel syndrome.
In medical terminology, “CTS” stands for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. However, in the auto industry, CTS refers to a line of luxury, automatic sedans manufactured by Cadillac. The CTS wagon was introduced to customers in 2008, and the CTS sedan followed in 2009. A tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) and four-wheel disc brakes are standard on all CTS models. The standard engine on the CTS is a 3.6-liter V6 that produces 263 horsepower. Previous engine options included a 2.8-liter V6 and a 3.6-liter V6 that were both discontinued in 2007. The fuel economy for the CTS depends on the engine and transmission combination. Rear-wheel drive is standard, but an all-wheel drive is an available option.
Have you been injured at some point in your journey?
Are you not achieving your highest level of function?
We’ve helped hundreds of people at all walks in life
get back to performing their best painfree!
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us




