Meniscus Injury
If you have been told by your doctor that you have a meniscus tear, then it is important to learn all you can about the injury and treatment options. This comprehensive guide will provide you with everything you need to know about meniscus tears, from causes and symptoms to treatment and recovery. You will also find advice on how to reduce your risk of developing a tear in the future. So whether you are just starting to research this injury or are preparing for surgery, read on for information and support.
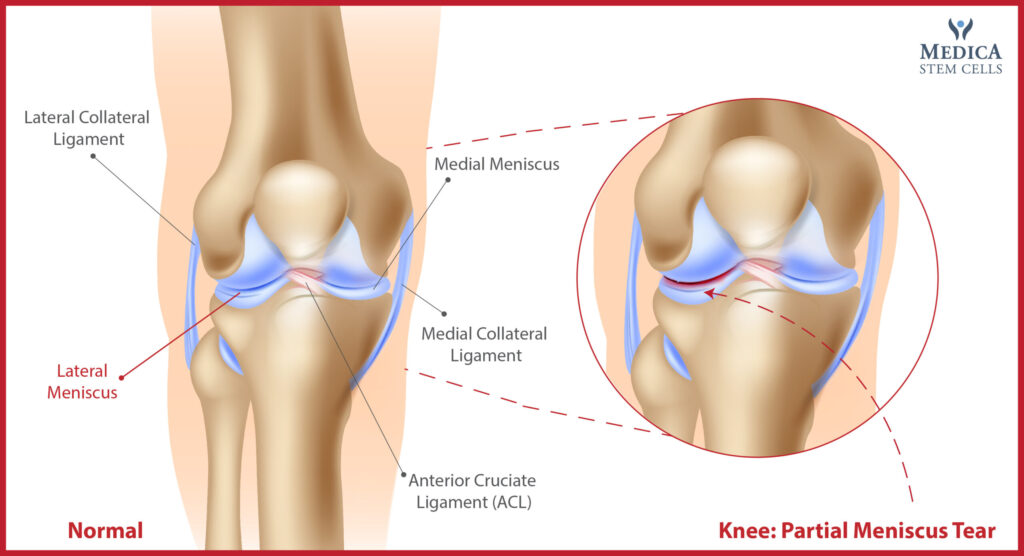
What is a meniscus tear?
A meniscus tear is an injury to the cartilage that cushions your knee. The cartilage may be torn by a sudden twisting motion or by gradual wear and tear.
A meniscus tear can occur in any age group but is most common in people over 40 years old. The risk of developing a meniscus tear increases with age and activity level.
Most meniscus tears are caused by degenerative changes due to wear and tear. However, a traumatic meniscal tear can occur from a sudden twisting motion of the knee. Meniscus tears are classified as either degenerative or traumatic.
Degenerative meniscus tears are the most common type of meniscus tear. They occur over time as the cartilage deteriorates with age and use. Degenerative meniscal tear is often seen in people over 40 years old.
Traumatic meniscus tears occur suddenly, often from a twisting motion of the knee. They can occur at any age but are most common in young athletes.
Symptoms of meniscus tears
Symptoms of a meniscus tear may include:
* Pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected knee
* A clicking or popping sensation
* Difficulty straightening the leg
* Knee weakness or instability
* A feeling of the knee “giving way”
If you have any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor.
Diagnosis of a meniscus tear
The diagnosis of a meniscus tear may include:
-A physical examination of the knee
-An MRI scan of the knee joint
-A arthroscopy (a minimally invasive surgery to look inside the knee joint)
-A knee X-ray
Your doctor may order one or more of these tests to confirm the diagnosis of a meniscus tear.
Treatment for a meniscus tear
The treatment for a meniscus tear will depend on the severity of the tear. The options include:
Rest:
This is the first line of treatment for a meniscus tear. You will need to take it easy and avoid any activities that put stress on your knee.
Ice:
Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time to help reduce swelling.
Compression:
Use an elastic bandage or compression sleeve to help keep the swelling down.
Elevation:
Prop your leg up on a pillow when you are sitting or lying down to help reduce swelling.
Medication:
Your doctor may prescribe pain medication or an anti-inflammatory drug to help with the knee pain and swelling.
Physical therapy:
A physical therapist can teach you exercises to help strengthen the muscles around your knee and improve your range of motion.
Arthroscopic surgery:
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery to repair the meniscal tear. The surgeon will make small incisions in the injured knee and insert a camera to see the damage. Then, they will use small tools to trim or sew up the torn meniscus.
Open surgery:
This is a more invasive surgery that may be necessary if the meniscal tears are large or complex. The surgeon will make a larger incision to access the meniscus and repair it.
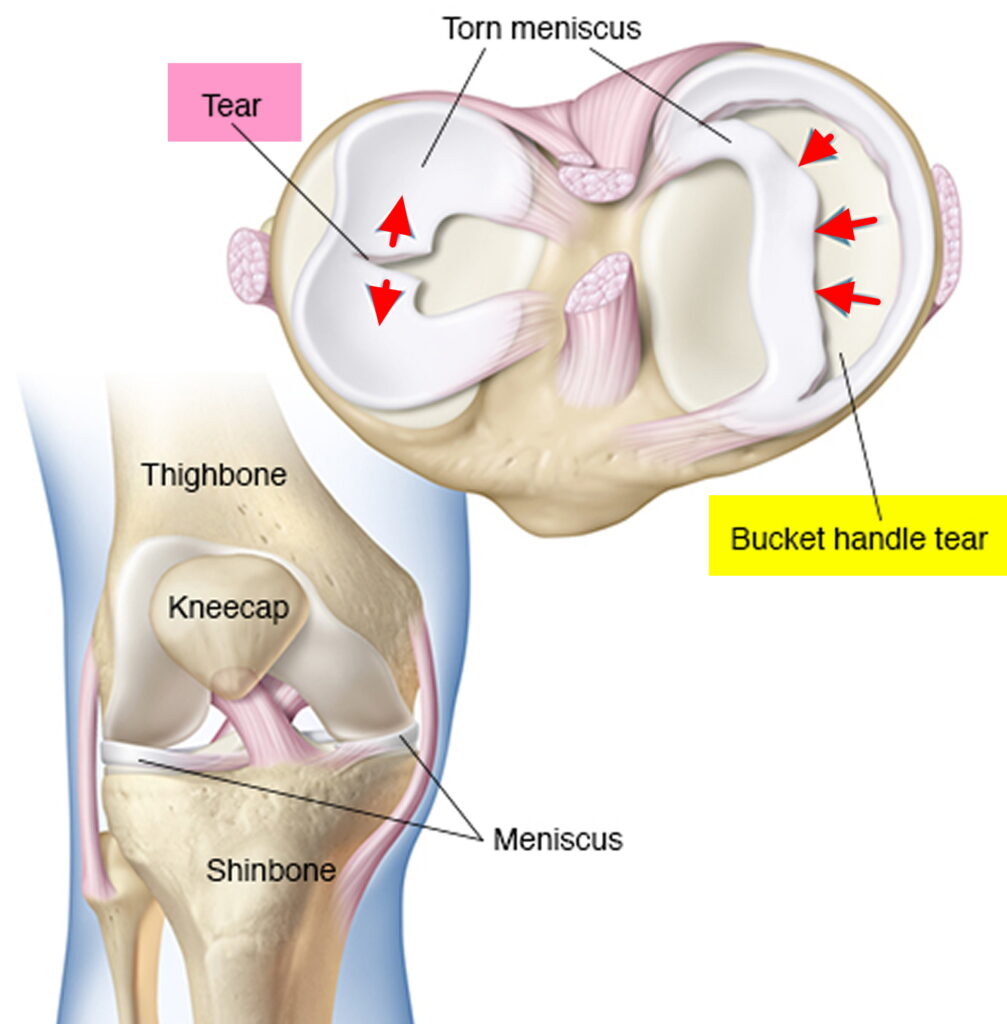
Tips to prevent meniscus tear
Following are certain tips that can help in preventing a meniscus tear and other most common knee injuries:
1) Improve your flexibility:
A good way to prevent meniscus tear and other knee injuries is by maintaining a good range of motion and flexibility in your joints. This allows your muscles to work more efficiently and also reduces the strain on your tendons and ligaments.
2) Strengthen your muscles:
Strong muscles help to stabilize your joints and prevent them from being overworked. It is especially important to focus on strengthening the muscles around your knees.
3) Wear proper footwear:
Wearing shoes that provide good support and cushioning can help reduce the stress on your knees. Avoid high-heeled shoes and instead opt for flat, comfortable shoes.
4) Be careful when exercising:
When participating in activities that put a strain on your knees, be sure to warm up properly first and use proper form. This will help reduce the risk of injury.
5) Avoid high-impact activities:
If you have had a previous knee injury or are at risk for one, it is best to avoid high-impact activities such as running or jumping. Instead, opt for lower-impact activities such as walking or swimming.
By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of suffering a meniscus tear. If you do experience an injury, be sure to seek medical attention right away.
Exercises to strengthen the knee
Following are some exercises that can help make your knees stronger.
1. Leg lifts:
Sit on the ground with both legs extended in front of you. Slowly lift one leg about 8 to 10 inches off the ground and hold it for a count of three. Lower the leg and repeat with the other leg. Do three sets of 10 repetitions for each leg.
2. Hamstring curls:
Lie on your back on the ground with both legs extended straight. Slowly bend one leg up towards your butt, keeping the other leg straight. Hold for a count of three and then lower the leg back down to the starting position. Repeat with the other leg. Do three sets of 10 repetitions for each leg.
3. Wall sits:
Stand with your back against a wall and your feet about shoulder-width apart. Slowly slide down the wall until your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Hold this position for 30 seconds to one minute. Repeat three times.
4. Lunges:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart and take a large step forward with one leg. Lower your body down so that your front knee is bent at a 90-degree angle and your back knee is almost touching the ground. Hold for a count of three and then push back up to the starting position. Repeat with the other leg. Do three sets of 10 repetitions for each leg.
5. Step-ups:
Stand in front of a stair or raised platform and place your left foot on the step. Step up with your left leg, bringing your right leg up to meet it. Return to the starting position and repeat with the other leg. Do three sets of 10 repetitions for each leg.
6. Squats:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart and lower your body down as if you were going to sit in a chair. Make sure your knees stay behind your toes and do not extend past your ankles. Hold for a count of three and then stand back up. Do three sets of 10 repetitions.
7. Calf raises:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart and raise up onto your toes, hold for a count of three and then lower back down.
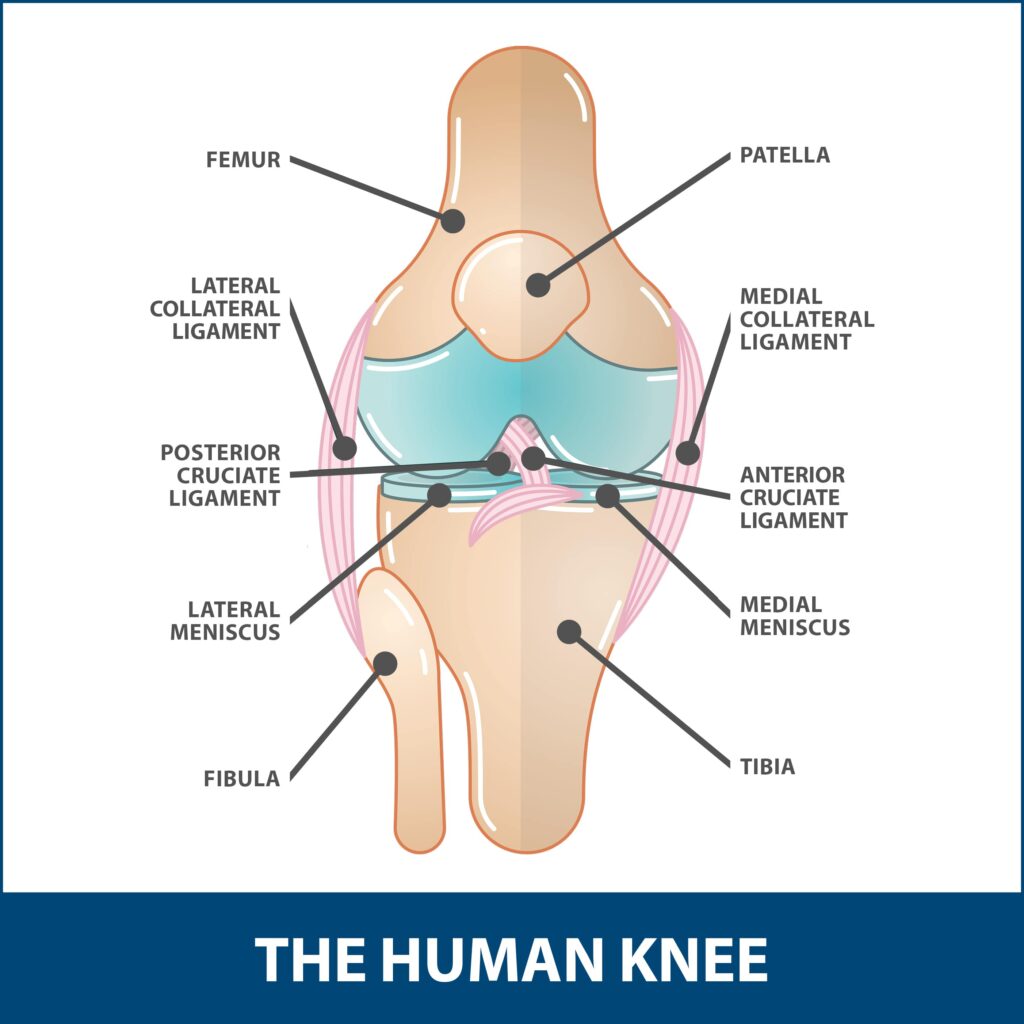
FAQs
The short answer is yes, a torn meniscus can heal on its own. However, it may not heal properly or completely, which could lead to more problems down the road. It’s always best to consult with a doctor or other medical professional to determine the best course of treatment. There are several options available for treating a torn meniscus, and the best option for you will depend on the severity of your injury. Surgery is usually only recommended for more severe tears that have not responded to other forms of treatment.
Yes, you can walk on a torn meniscus. However, it is important to see a doctor if you think you may have this injury. Walking on a torn meniscus can cause further damage to the knee joint and lead to more pain. A doctor can help diagnose the problem and develop a treatment plan that is best for you.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best treatment for a meniscus tear will vary depending on the individual case. However, some common treatments for meniscus tears include rest, ice, sports medicine, and physical therapy. Surgery may also be necessary in some cases.
A torn meniscus is a common knee injury. The meniscus is a crescent-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion between the bones in your knee. A tear in the meniscus can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. If left untreated, a torn meniscus can lead to further damage to the cartilage in your knee and eventually to arthritis. Treatment for a torn meniscus usually involves surgically repairing or removing the damaged cartilage.
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us




