CORE MUSCLE INJURY (SPORTS HERNIA)
PELVIS
CORE MUSCLE INJURY
AKA SPORTS HERNIA
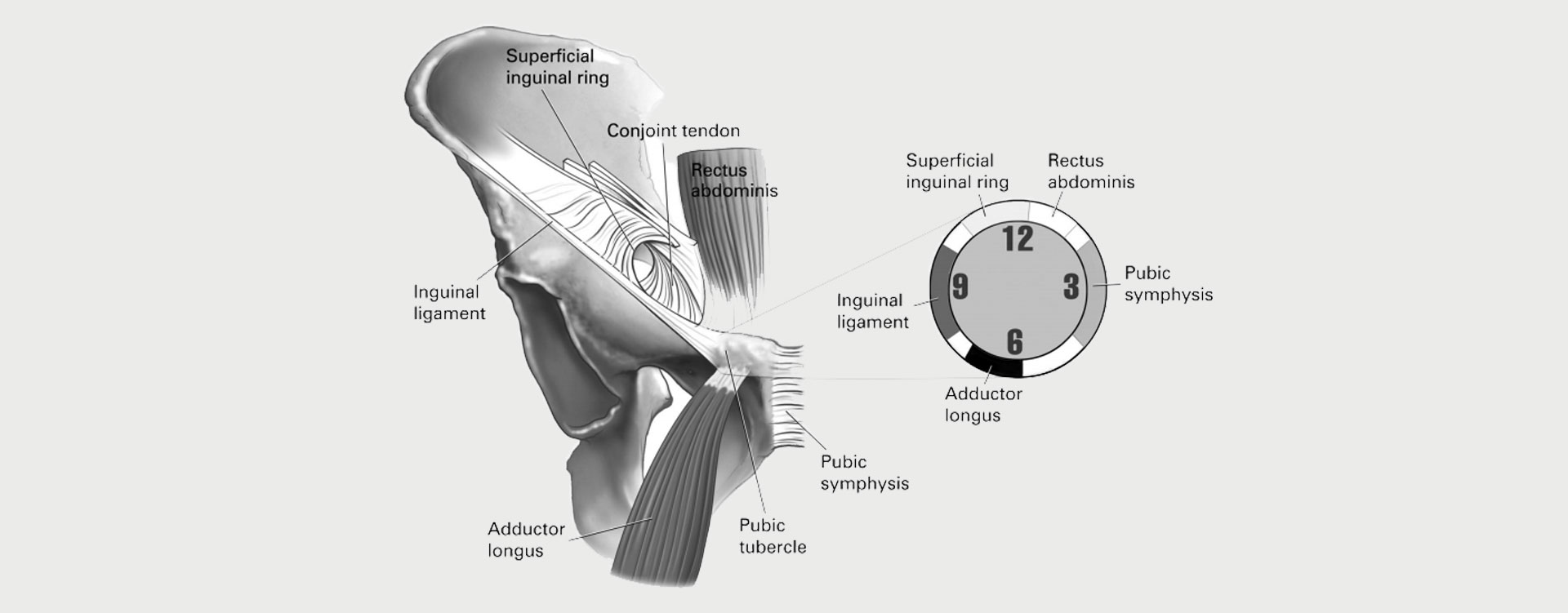
A sports hernia is not to be confused with a regular hernia, where the muscular wall weakens enough to allow the abdominal organs and tissues to push through. In a sports hernia, there is no visible bulge. Instead, these common athletic injuries have to do with tears deep in the abdominal wall, where the abdominal muscles attach to the pelvis.
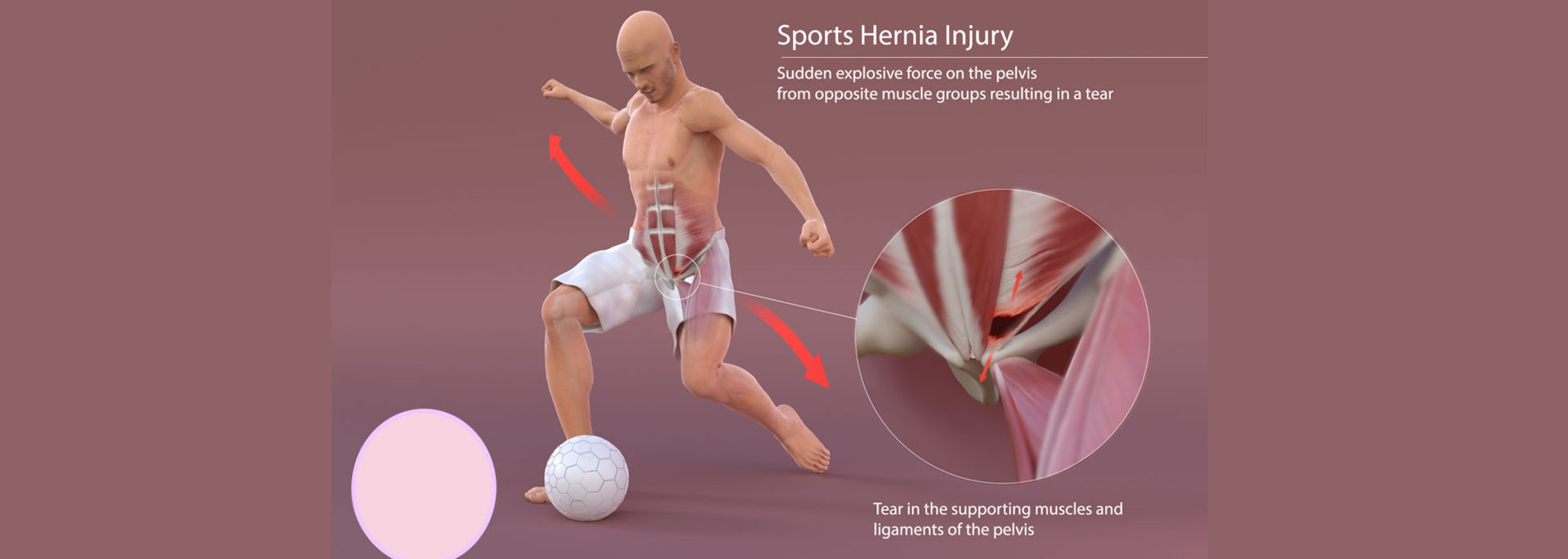
A core muscle injury — also known as pubalgia — gets its misleading nickname because of the symptoms it has in common with an actual abdominal hernia. There can be an intense, sharp pain in the groin region, usually isolated to a specific area. It’s usually very tender, and gets worse when coughing, sneezing, or in the midst of physical activity.
Groin pain is an extremely common occurrence among athletes, so we’ve treated countless cases at MOTUS. People who play sports that call for a specific use of the lower abdominal muscles are affected the most. We usually see a core muscle injury in athletes who play soccer, ice hockey, rugby, football, or track. Essentially, any sport that requires repetitive twisting, kicking, or cutting movements can lead to a core muscle injury.
Many times, pubalgia develops as a result of an imbalance between the hip muscles and the abdominal muscles. Every joint is surrounded by muscles that work together to keep the joint centered.
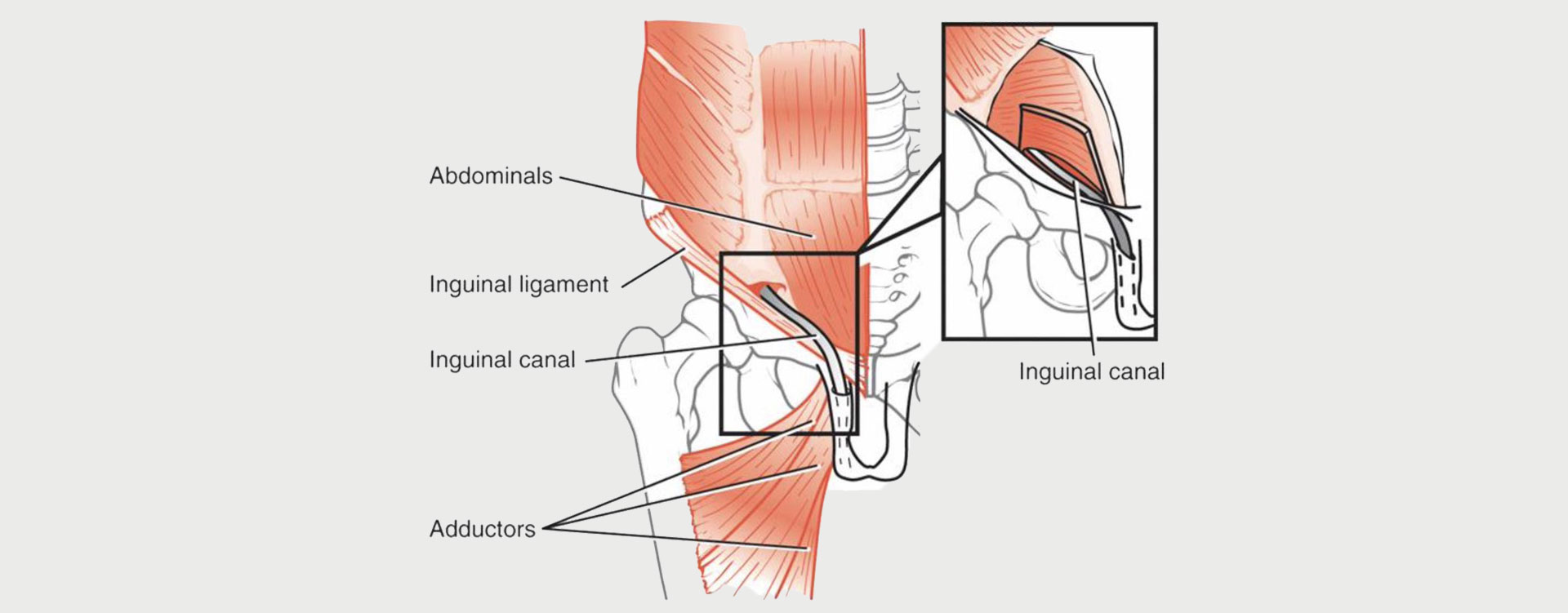
When the muscles are balanced in strength and flexibility, they provide the optimum movement. If they’re imbalanced, it can lead to an inequality of forces that can cause a tear.
Since imbalance is one of the biggest causes of a core muscle injury, it’s important to look at the body as a whole when treating this condition. At MOTUS, we consider ourselves to be movement specialists, and take pride in prioritizing not just the area in pain but the entire body. We want to correct that imbalance in the hip muscles and abdominal muscles through education, as well as strengthening and flexibility exercises.
However, we can’t always immediately start with increased physical activity. Treatment for a core muscle injury, as with any condition, needs to be specific to the athlete. Sometimes we need to start by improving symptoms with rest and methods like NMES, shockwave therapy, or hot and hold therapy. These treatments can help reduce exercise-induced groin pain. In most cases, conservative treatment through physical therapy is enough to get you back to your normal activity level.c
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us




